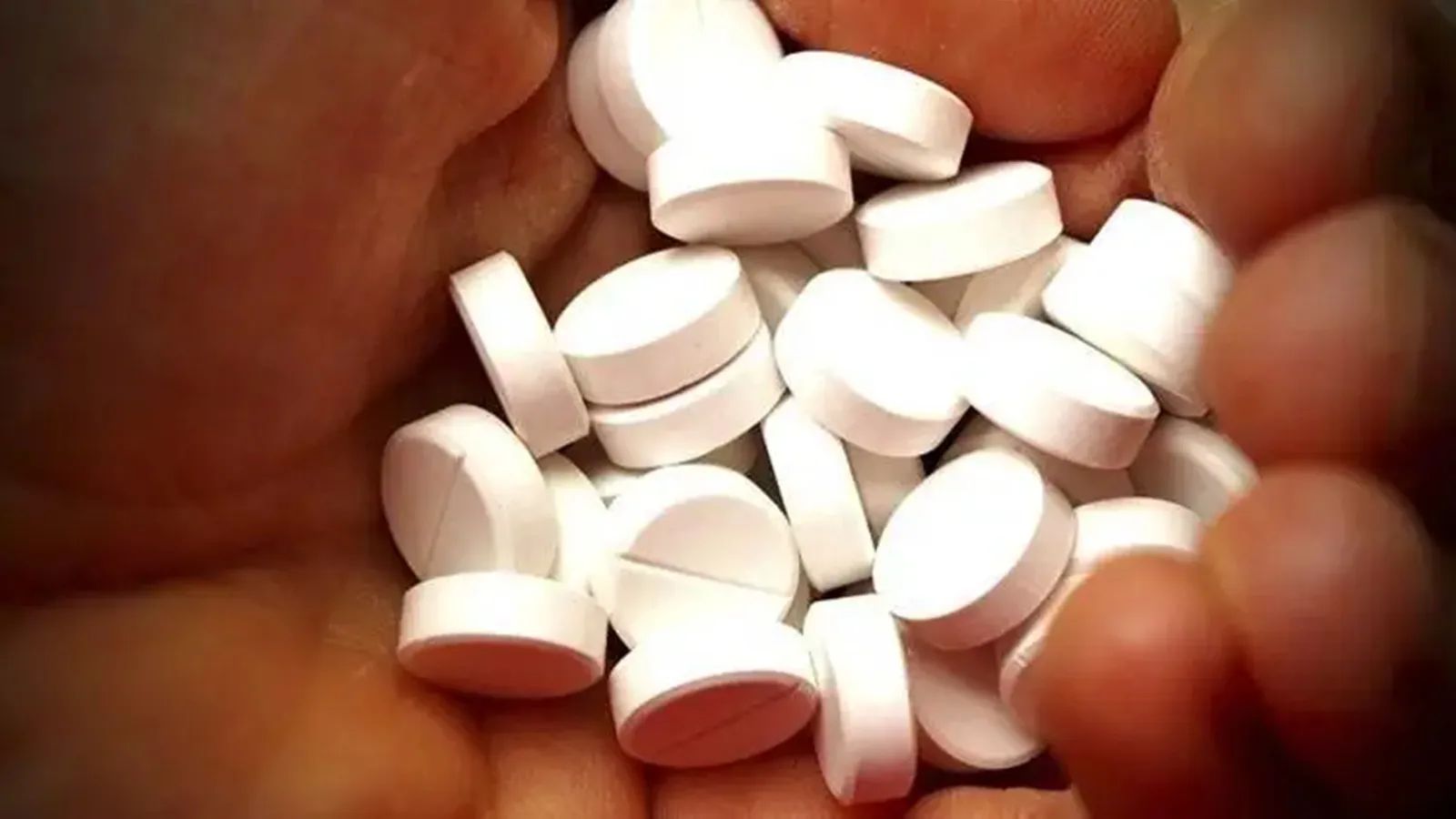
Painkillers are among the most commonly used medications worldwide. From over-the-counter options to prescription drugs, they offer quick relief from a variety of ailments, such as headaches, muscle aches and chronic pain conditions. However, while they can be effective in alleviating discomfort, their excessive or improper use can lead to significant health issues, particularly those of the stomach and kidneys. Painkillers can be broadly classified into two main categories: non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and opioids. NSAIDs work by reducing inflammation and blocking pain signals in the body. Opioids, on the other hand, interact with the nervous system to relieve severe pain but come with a higher risk of dependency and adverse effects. Prolonged use of NSAIDs results in gastrointestinal (GI) complications. The risk of these conditions increases with higher doses, prolonged use and the use of multiple medications. Additionally, individuals with a history of GI issues, older adults and those who consume alcohol may be more susceptible to these side effects. The kidneys play a crucial role in filtering waste from the blood and maintaining fluid balance. Chronic painkiller use, particularly NSAIDs and certain prescription medications, can strain the kidneys, leading to various health complications: Consult a doctor when you develop symptoms such as persistent abdominal pain, changes in bowel habits, swelling in the legs or ankles, fatigue and decreased urine output after you have had painkillers. Best Practices for Safe Painkiller Use To mitigate the risks associated with painkiller use, consider the following recommendations: (Dr Chatterjee is internal medicine specialist at Indraprastha Apollo Hospitals, New Delhi) None
Popular Tags:
Share This Post:
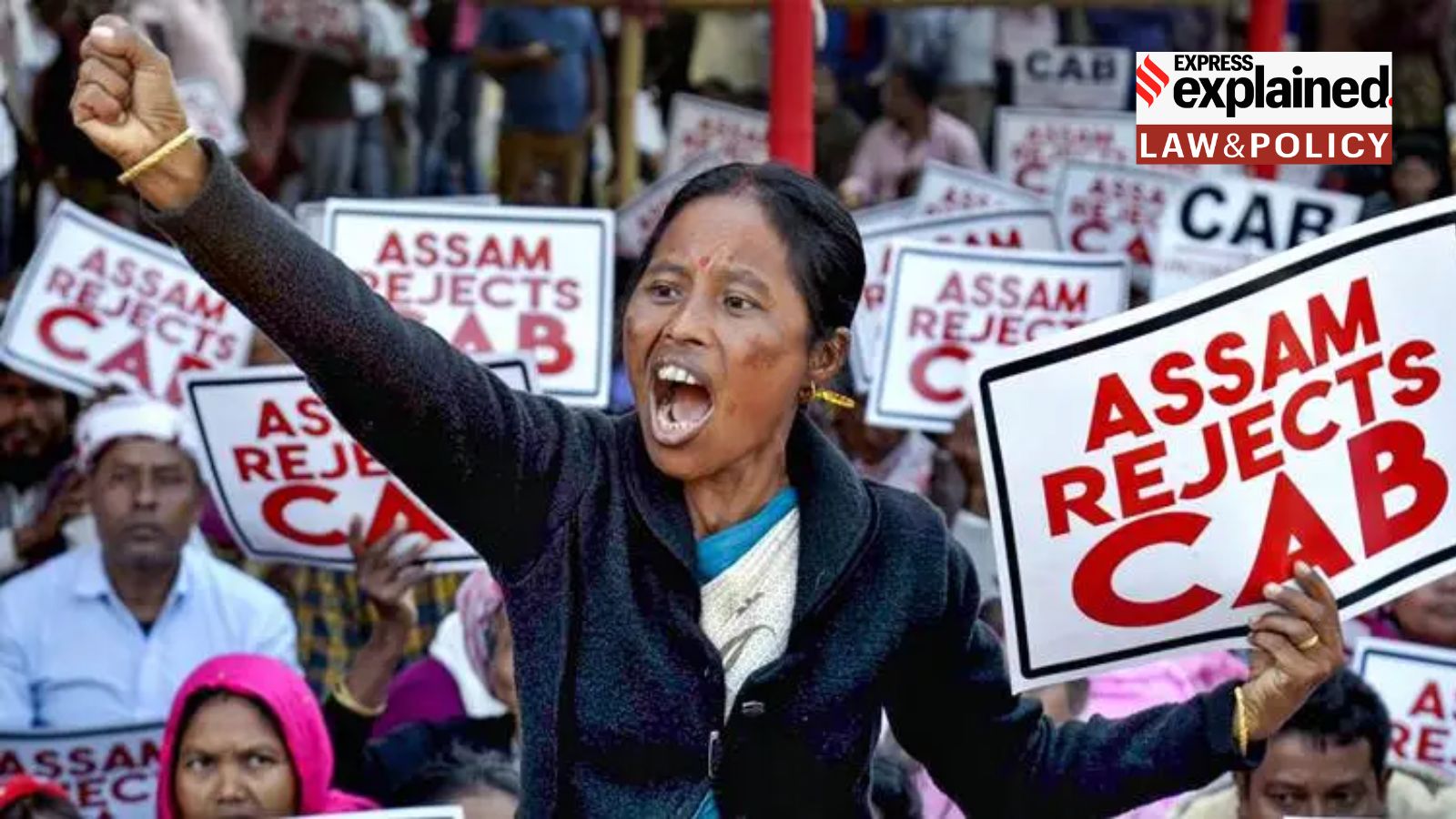
SC to rule on legality of Citizenship Act provision in Assam
- by Sarkai Info
- October 17, 2024

What’s New
Spotlight
Today’s Hot
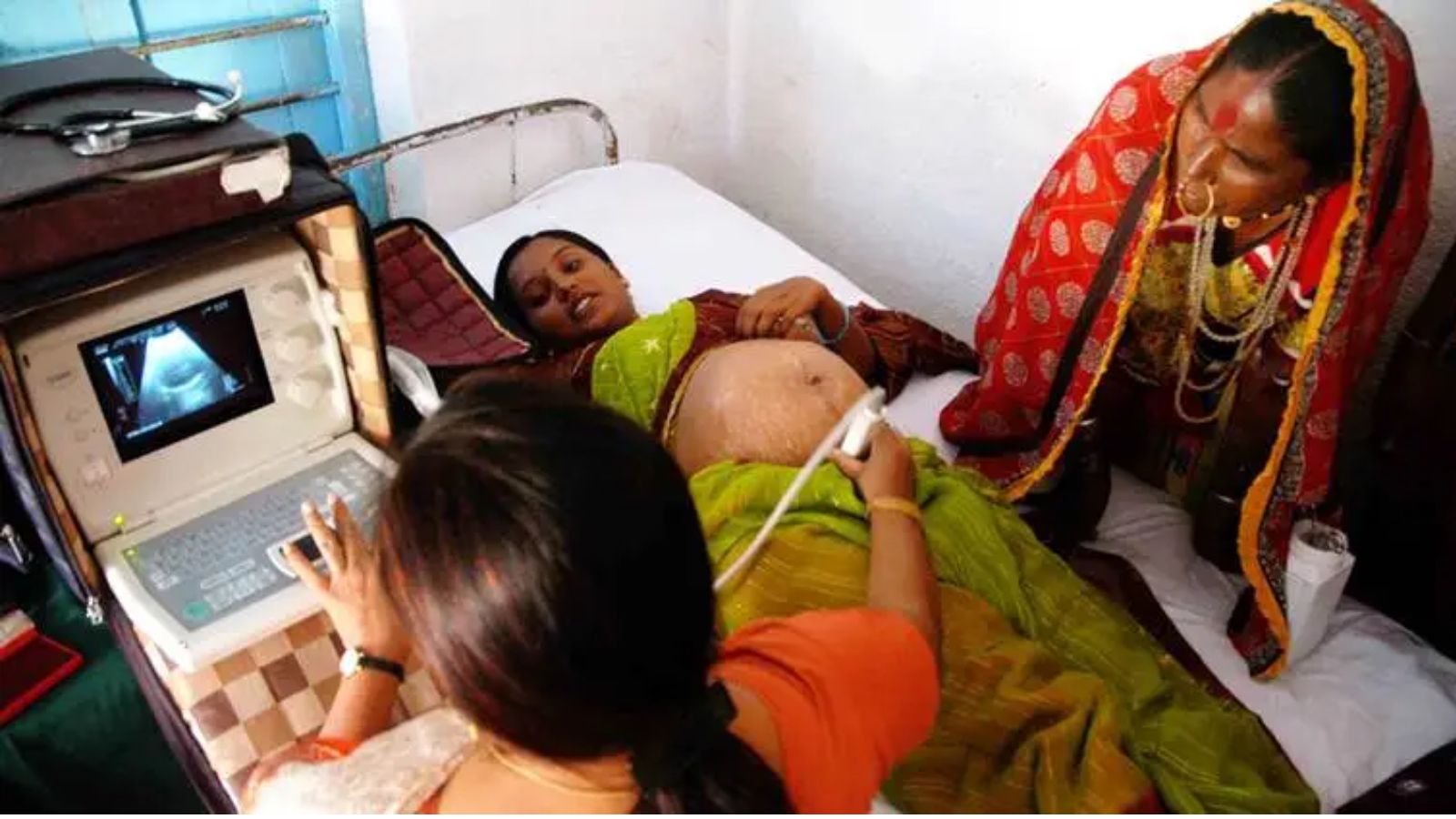
The spread of sex selection in India: Not just the foreign hand
- By Sarkai Info
- October 17, 2024
Featured News
Is overusing painkillers harming your stomach and kidney?
- By Sarkai Info
- October 17, 2024
Why climate change is a national security issue
- By Sarkai Info
- October 17, 2024
Latest From This Week
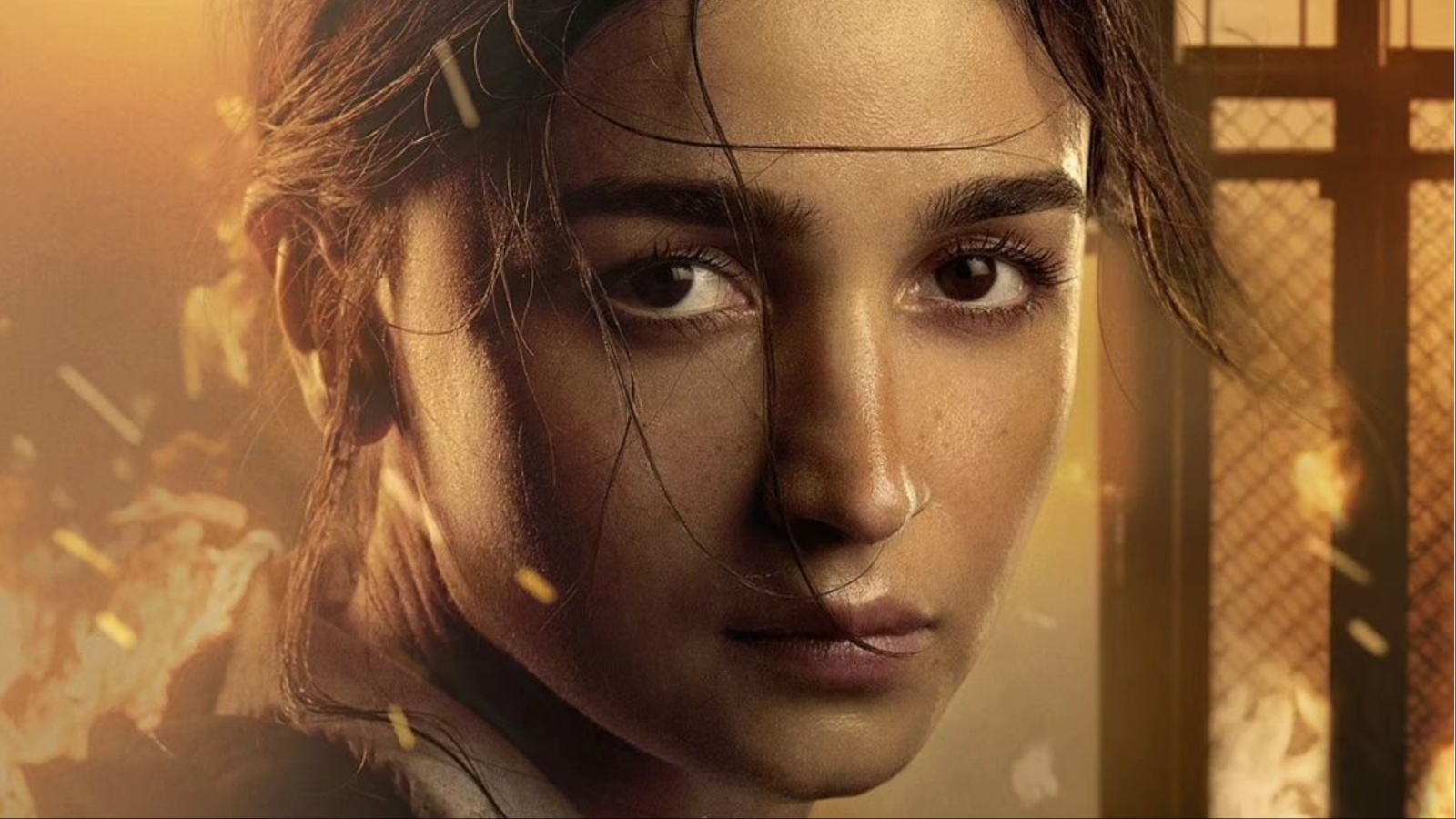
Vasan Bala’s unabashed cinephilia nearly salvages a lacklustre Jigra
ARTICLE
- by Sarkai Info
- October 17, 2024
Subscribe To Our Newsletter
No spam, notifications only about new products, updates.